Eukaryotes are the cells that contain cells having the nucleus and also have the organelles that are bounded with membranes. Eukaryotes are organisms whose cells contain a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles.
The cells of the eukaryotes have chromosomes that are seen in the nucleus of the cell. The eukaryotic chromosome structure has DNA inside of the nucleus in the molecule of the DNA and is quite packed up tight around proteins having many proteins that are coiled up called the histones.
There are many eukaryotic cells that have many chromosomes being multiple in number that are linear in its shape. There can be much difference in the cell format for eukaryotic chromosome structure and the prokaryotes with bearing a difference in size and being much linear in its molecular format. The cells do have a good maintained nucleus. An array of holes, or pores, in the nuclear membrane allows for the selective passage.

The eukaryotic chromosome structure has a good defined organelle with some examples being the fungi, animals’ plants and protists. The genetic material is much organized in the chromosome. This also forms a good part of the eukaryotic chromosome structure along with differing much in the structure of the prokaryotes. A nucleus, as related to genomics, is the membrane-enclosed organelle within a cell that contains the chromosomes.
Are eukaryotic chromosomes circular or linear?
There are two types of organism being the prokaryotic and the eukaryotic ones with having different features. This type of DNA is found in the cytoplasm of most prokaryotic cells. Also, it is seen in organelles like chloroplasts and mitochondria.
The eukaryotic chromosome structure along with differing much in the structure of the prokaryotes have its chromosome to be in the linear shape while prokaryotes have it as circular form. The size of the eukaryotic chromosome structure is larger than the prokaryotes as they are bigger in size than that of prokaryotes.
The number of eukaryotic chromosome structure is counted in multiple form with the other being single in number. The eukaryotic chromosome structure is much complex and is seen in the nucleus. At the very basic level for the eukaryotic chromosome structure the chromosome is called to be the molecule of the DNA that is much tightly packed and coiled said to be histones.
The eukaryotic chromosome structure has a shape that is linear and has many number of chromosomes with humans also having linear shape cause they are eukaryotes and thus have eukaryotic chromosome structure along with have multiple variations in its cell type and is located in the nucleus. The difference for eukaryotic chromosome structure and prokaryotes are many.
Why eukaryotic chromosomes are linear?
Any chromosome that is linear is cause for its shape and also has terminal ends in its way and form mostly is eukaryotes.
The eukaryotic chromosome structure has linear and many chromosomes arranged in multiple form with varying in traits and are arranged in the DNA inside the nucleus. The prokaryotes like bacteria do have the shape of chromosome that is contradicting from eukaryotic chromosome structure and is thus circular.
The eukaryotic chromosome structure is much compact in its form alog with having the protein called as histones and also has many telomeres ant the end of the form to protect itself from the deterioration. On addition to it the v is separate from the prokaryotes for its size and function of the organism along with having DNA that is transferable and has plasmids.
The eukaryotic chromosome structure differs from the prokaryotes for they have DNA that is double stranded and also the eukaryotes have many chromosomes that are linear in shape along with having chromatin and is surrounded by the nuclear membrane. The bacteria do have a circular chromosome with being only one in number yet it is made of the single chromosome.
What does a chromosome look like in eukaryotic cell?
All of the cells in the eukaryotic chromosome structure do have a nucleus and thus they are linear in its form and function in same way as other.
The very framework for eukaryotic chromosome structure is it having chromosomes that are made of chromatin and also have strands of DNA that is complementary in DNA and thus also have coiled proteins called histone tightly packed. The molecule of DNA in the eukaryotic chromosome structure is linear.
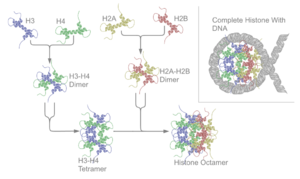
In the eukaryotic chromosome structure the helical format of the DNA shape makes it up for each of the chromosomes and is first coiled around the histone protein cluster. The eukaryotic chromosome structure has a unit of around being 200 DNA base pair and also wind around the eight protein position making the smallest unit of DNA in eukaryotic chromosome structure.
The eukaryotic chromosome structure is seen in the cell and is stored in the place called the nucleus. Each of them have the eukaryotic chromosome that is made up of the coiled DNA and also has a condensed form around the proteins in the nucleus called the histones. This helps in the eukaryotic chromosome structure differing from the prokaryotes.
How are chromosomes arranged in eukaryotic cells?
The eukaryotic chromosome structure is much in linear way and also has many number of chromosomes in it with being packed up to full.
The genetic material in the eukaryotic chromosome structure is seen in the DNA and mostly said in the nucleus being linear in its shape. The eukaryotic chromosome structure is made of the complex protein in DNA and is called the chromatin that is organized in subunits called as the nucleosomes.
There are 46 number of chromosome in the eukaryotic chromosome structure with 23 pairs and the total of 22 pairs is called the autosomes while other is for reproduction in the eukaryotic chromosome structure. They are labelled in the format of 1-22 for the reference stiff. Each of the eukaryotic chromosome structure pairs to have one chromosome that is inherited from both the parents.
The cells of the prokaryotes are different from the eukaryotic chromosome structure and thus have a chromosome that is circular and is seen in the nucleoid and the prokaryotes have mostly single nucleus and is singular with the circular chromosome being able to replicate faster than the one sin the eukaryotic chromosome structure for less in work and use.
How is the structure of a eukaryotic chromosome during mitosis?
The DNA of theeukaryotic chromosome structure is double helical in pattern with having many protein clusters called histones.
The smallest unit of base paring for the histones is seen in the nucleosomes packed in the place with making the fact for the cells of the prokaryotes are different from the eukaryotic chromosome structure being true. There is a surety for 200 DNA pairs in it and is condensed in form.
The cells of the prokaryotes are different from the eukaryotic chromosome structure mostly for its size and thus the eukaryotic chromosome structure is said to be packed up needed a good amount of high condense packing for the DNA molecules in the nucleus of the cell with much wide amount of the DNA. The packing level for eukaryotic chromosome structure has histones too.
The eukaryotic chromosome structure packing contains having the DNA wrapped up in histones that are the proteins in the nucleus along with them being in order to make nucleosomes that are condensed in the eukaryotic chromosome structure. There are many proteins that tend to compact this nature fir eukaryotic chromosome structure into minute space.
Is eukaryotic chromosome double stranded?
The DNA for the prokaryotes are much compact and this is how the eukaryotic chromosome structure is in difference with rest with being a double helix.
There are proteins called histones within the space of DNA and thus the protein is much complex made with chromatin and thus also seems to be paradox along with having a eukaryotic chromosome structure with packed double helix DNA making it much tight coiled up.
In the eukaryotic chromosome structure, the organizing manner for the DNA is 3 is form that has the chain of the nucleosomes, the super base or the solenoidal nucleomere model of the nucleus fiber that is compacta and at last the mode of having the domains or the loops packed up in eukaryotic chromosome structure. Chromosomes are thread-like structures located inside the nucleus of animal and plant cells.
There is also a term for the true eukaryotes for that concerns to the eukaryotic chromosome structure having the protein and DNA together. The pattern for eukaryotic chromosome structure is to have the histones seemingly and compact around the DNA and do tend to be seen as beads of the string having a fiver in eukaryotic chromosome structure. Passed from parents to offspring, DNA contains the specific instructions that make each type of living creature unique.
How are chromosomes compacted?
At the time of few stages in the cell, there is a long list of DNA strands that are in compact form to get in place. Each person normally has one pair of reproduction chromosomes in each cell
The eukaryotic chromosome structure is called to be a thread like frame that is seen in the animals and the cells of plants inside the nucleus. Each of the eukaryotic chromosome structure do have protein and also have DNA said to be the vital part of eukaryotic chromosome structure with specific to the organism and its need.
The eukaryotic chromosome structure has a stage specified compacted formation of the chromosome in order to fir in the eukaryotic chromosome structure. In the 1st level of the compact shape, there are short stretch for the double helical wrap and a core of histones shall be in right form along the whole length of the eukaryotic chromosome structure.

Most eukaryotic chromosomes include packaging proteins called histones which, aided by chaperone proteins, bind to and condense the DNA molecule to maintain its integrity. Females have two X chromosomes, while males have one X and one Y chromosome. Early in embryonic development in females, one of the two X chromosomes is randomly and permanently inactivated in cells other than egg cells.
What are eukaryotes & prokaryotes?
All of the living organism terming from being to small are said to be made of cells. Some of them are just like the bacteria that is made of single ones.
There are some of the organism like prokaryotes that have one cell while the rest have many or in billion just like in the eukaryotic chromosome structure. All of the organism can be divided into 2 groups based on the structure of cell and thus the term eukaryotic chromosome structure.
Archaea and bacteria are called the prokaryotes that are based on the fundamental separation factor in the cell area. All of the rest being fungi, protists, humans, animals and plants are eukaryotic chromosome structure. The prokaryotes are said to be unicellular while the eukaryotes are called to be the multicellular ones or the ones with single cell.
Both of them tend to have a cell membrane and also has a bilayer of lipid and show much difference that keeps the cell contents away and differing from each other. Thus the eukaryotic chromosome structure and prokaryotic ones differ as well. The membrane is to have the control over all the substances to move in and out of the cell in any form. Identifying genes on each chromosome is an active area of genetic research.
What is the function of eukaryotic chromosome?
The chromosomes of the eukaryotic chromosome structure ranges from billions in number for there are many cells in them. Chromosomes are found in the nucleus of each cell.
The eukaryotic chromosome structure is seen in the nucleus while the prokaryotes have it in the nucleoid. The eukaryotic chromosome structure has all organelles with membrane. The primary function for the eukaryotic chromosome structure are to-
- Act as a vehicle for hereditary
- Get the control of the metabolism and cell division
- Getting the control of the DNA in form of genes
- Help in replication
- Takes part in cell differentiation
- Store generic data
- Transmit of the genetic DNA to other cell
Just unlike the ones in the prokaryotes the eukaryotic chromosome structure is made of the molecules of DNA that is linear in shape. They are much vital and is seen in the nucleus having a layer double in frame to have the organelles in the cell protected. This double layer in eukaryotic chromosome structure is called the nucleus membrane. Chromosomes are found in the nucleus of each cell.
At the time of cell division, the eukaryotic chromosome structure is said to be much coiled up with being dense in form as well and its features. The coiling being tight has a good level of degree in the DNA supercoiling form and thus facilitates the good or better segregation of eukaryotic chromosome structure and also has high pattern of organization.
Why are eukaryotic chromosomes not circular?
DNA is arranged in multiple linear chromosomes. In contrast, most prokaryotic cells generally contain a singular circular chromosome. the eukaryotic chromosome structure is mostly said to be linear in all ways.
Strictly speaking, all nucleated or the eukaryotic cells contain linear DNA. In addition to the nucleus, the mitochondria which break down food molecules and create chemical energy and chloroplasts which facilitate photosynthesis also have small stores of their own DNA and this DNA is circular. Thus the eukaryotic chromosome structure is mostly said to be linear in all ways.
Extrachromosomal circular DNA or the eccDNA is ubiquitous in eukaryotic organisms, and has been noted for more than 3 decades. eccDNA occurs in normal tissues and in cultured cells, is heterogeneous in size, consists of chromosomal sequences and reflects plasticity of the genome. Linear DNA is the DNA with two ends on each side of the DNA molecule.

It shows that most eccDNA consists of chromosomal tandem repeats, both coding genes and satellite DNA and is organized as circular multimers of the repeating sequence. 2D gels were unable to detect dispersed repeats within the population of eccDNA. These findings support a mechanism for the formation of eccDNA that involves intra-chromosomal homologous recombination for eukaryotic chromosome structure.
Example of eukaryotic cell
Some of the examples for eukaryotic chromosome structure are-
- Animal cell
- Plant cell
- Fungus
- Paramecium
- Protozoa
Animal cell
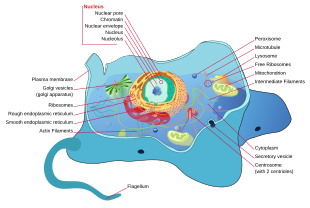
On the basis of the cellular organization, cells are further classified as eukaryotic and prokaryotic. Plant cells and animal cells fall under the eukaryotic category.
The largest known animal cell is the ostrich egg, which can stretch over 5.1 inches across and weighs about 1.4 kilograms. This is in stark contrast to the neuron in the human body, which is just 100 microns across. Most of the cells are microscopic in size and can only be seen under the microscope along with also the eukaryotic chromosome structure.
Animal cells are the basic unit of life in organisms of the kingdom Animalia. They are eukaryotic cells, meaning that they have a true nucleus and specialized structures called organelles that carry out different functions. A cell carries out all the processes of the body which includes producing energy and storing it, making proteins which are molecules that have roles in metabolism and DNA replication.
Plant cell
Plant cells, like animal cells, are eukaryotic, meaning they have a membrane-bound nucleus and organelles. Cells are membrane-bound groups of organelles that work together to allow it to function.
The parts of a plant cell and plant cell components, which will be discussed, are plant cell wall, plant cell membrane, smooth endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, rough endoplasmic reticulum, vacuole, nucleus, peroxisomes, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, and plastids classified under the eukaryotic chromosome structure.
Plant cells are the basic unit of life in organisms of the kingdom Plantae. They are eukaryotic cells for under the category on eukaryotic chromosome structure. Plant cells have a cell wall. Plant cells are different from animal cells in a number of ways. · Plant cells contain vacuoles.
Fungus
A fungus is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms.
There are also many fungus like organisms, including slime molds and oomycetes. Many of these fungus like organisms are included in the kingdom Chromista. Fungi are among the most widely distributed organisms on Earth and are of great environmental and clinical importance.
Fungi are among the most widely distributed organisms on Earth and are of great environmental and medical importance. Many fungi are free-living in soil or water; others form parasitic or symbiotic relationships with plants or animals. Fungi are eukaryotic organisms; i.e., their cells contain membrane-bound organelles and clearly defined nuclei.

Paramecium
Paramecium or paramecia are single-celled protists that are naturally found in aquatic habitats. They are typically oblong or slipper-shaped and are covered with short hairy structures called cilia.
A paramecium is not a fungus. A fungus can be single or multi-celled. All fungi are eukaryotic, which means that their cells don’t have a nucleus. Paramecia have no eyes, no heart, no brain, and no ears. Paramecia are able to undergo reproduction and digestion even without many of the systems in other organisms.
When a paramecium ingests food it also ingests water, which is pumped out via the vacuole pumps. A paramecium killed by iodine, displaying cilia and trichocysts. Their small size and easy culturing make paramecia an ideal classroom organism. Paramecia play a role in the carbon cycle because the bacteria they eat are often found on decaying plants.
Protozoa
The mature cell divides into two cells and each grows rapidly and develops into a new organism. Under favourable conditions, Paramecium multiplies rapidly up to three times a day.
Most species can be cultivated easily in the laboratory, making them ideal model organisms, well suited for biological study. Paramecia are hearty organisms found living in almost all types of water bodies.
Paramecium species are found in both fresh and salt water, and some can live in moist soil or even in other organisms.
Conclusion
The eukaryotic chromosome structure has linear chromosome with DNA along with having in the nucleus and is seen in the multiple forms.
Also Read:
- Obligate parasite
- Cytoskeleton function
- Plant enzyme example
- Are proteins peptides
- Is nucleus a cell organelle
- Monophyletic group example
- Is protease an enzyme
- Difference between animal and plant cell chromosomes
- Chromatin vs chromatid
- Scorpion examples
I am Ankita Chattopadhyay from Kharagpur. I have completed my B. Tech in Biotechnology from Amity University Kolkata. I am a Subject Matter Expert in Biotechnology. I have been keen in writing articles and also interested in Literature with having my writing published in a Biotech website and a book respectively. Along with these, I am also a Hodophile, a Cinephile and a foodie.
