Seismic waves are vibrations that travel through the Earth’s layers, caused by energy released during earthquakes or other geological events. The velocity of seismic waves refers to the speed at which these waves propagate through the Earth. Understanding how to find the velocity of seismic waves is crucial for studying the Earth’s structure and predicting the behavior of earthquakes. In this blog post, we will explore the factors affecting the velocity of seismic waves, the calculations involved, and compare the velocities of different types of seismic waves.
Factors Affecting the Velocity of Seismic Waves
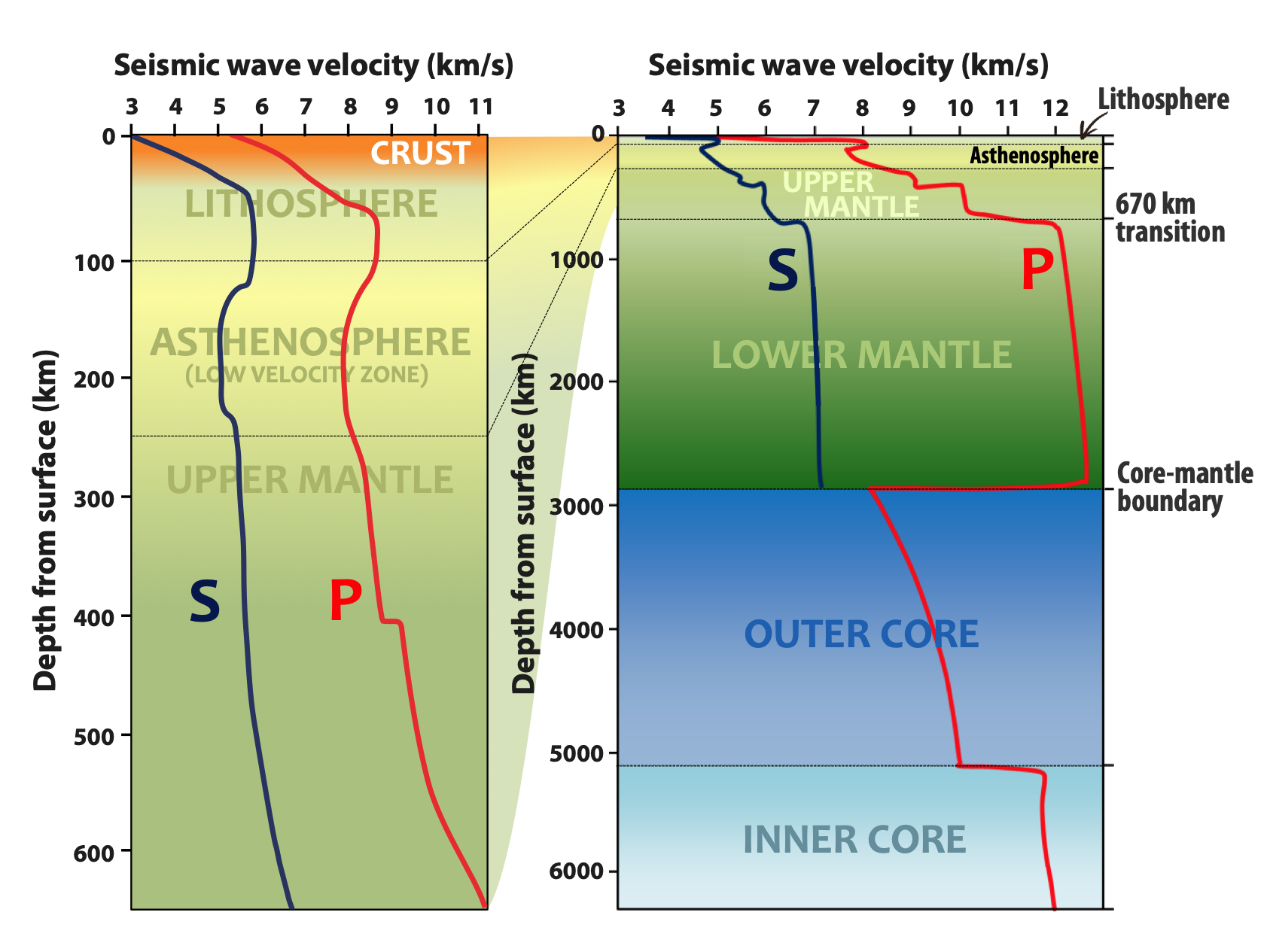
Depth in the Lower Mantle
The velocity of seismic waves varies depending on the depth within the Earth’s layers. In the lower mantle, the velocity increases with depth. This increase is primarily due to the increase in pressure, which causes the materials to become more compact and tightly packed. As a result, the seismic waves travel faster at greater depths in the lower mantle compared to shallower regions.
Material Properties
The velocity of seismic waves also depends on the properties of the materials through which they pass. Different materials have different densities, elastic properties, and compositions, all of which affect the speed of seismic wave propagation. For example, seismic waves travel faster through solid rocks compared to fluids like water or molten lava. This is because solids transmit compressional waves more efficiently due to the interconnected nature of their molecules.
Changes in the Speed of Seismic Waves
Seismic waves can experience changes in velocity when they encounter boundaries between different layers with distinct material properties. These boundaries can cause the waves to reflect, refract, or even diffract, leading to variations in their speed. The phenomenon of seismic wave reflection occurs when waves bounce off a boundary, while refraction refers to the bending of waves as they pass through a different medium. These changes in direction can influence the overall velocity of seismic waves.
Calculating the Velocity of Seismic Waves


To calculate the velocity of seismic waves, we can use the following formula:
![]()
Where:
– V represents the velocity of seismic waves,
– D is the distance traveled by the wave, and
– T is the time taken for the wave to travel that distance.
Let’s work through an example to illustrate how this formula is applied.
Worked Out Example on How to Calculate the Velocity of Seismic Waves

Suppose a seismic wave travels a distance of 100 kilometers and takes 10 seconds to complete that journey. We can calculate its velocity using the formula mentioned earlier:
![]()
Therefore, the velocity of the seismic wave in this example is 10 kilometers per second.
Comparing the Velocity of Different Types of Seismic Waves
Which Type of Seismic Wave has the Fastest Velocity
There are three main types of seismic waves: P-waves, S-waves, and surface waves. Among these, P-waves, also known as primary waves or compressional waves, have the fastest velocity. P-waves travel through both solids and fluids and are characterized by their ability to compress and expand the material they pass through. Their faster velocity allows them to reach seismometers before other waves during an earthquake, making them the first to be detected.
Where Do Seismic Waves Travel the Fastest
Seismic waves travel at different speeds depending on the characteristics of the Earth’s layers they encounter. Generally, seismic waves travel fastest through solid materials, such as rocks, compared to fluids or loose sediments. This is because solids have a higher density and are better able to transmit wave energy. Therefore, seismic waves tend to travel fastest in the Earth’s solid crust and upper mantle.
Understanding the velocity of seismic waves is essential for studying the Earth’s structure and predicting the behavior of earthquakes. Factors such as depth, material properties, and interactions with boundaries can all influence the speed at which seismic waves propagate. By calculating the velocity of seismic waves and comparing the velocities of different types of waves, scientists can gain valuable insights into the Earth’s interior and improve our ability to assess and mitigate seismic risks.
Numerical Problems on how to find velocity of seismic waves

Problem 1:
A seismic wave travels through a medium with a frequency of 10 Hz and a wavelength of 10 m. Calculate the velocity of the seismic wave.
Solution:
We know that the velocity of a wave is given by the formula:
![]()
where
– ![]() is the velocity of the wave,
is the velocity of the wave,
– ![]() is the frequency of the wave, and
is the frequency of the wave, and
– ![]() is the wavelength of the wave.
is the wavelength of the wave.
Substituting the given values into the formula, we have:
![]()
Therefore, the velocity of the seismic wave is 100 m/s.
Problem 2:
A seismic wave with a velocity of 2000 m/s travels through a medium with a wavelength of 20 m. Determine the frequency of the seismic wave.
Solution:
Using the formula for wave velocity:
![]()
we can rearrange the formula to solve for frequency:
![]()
Substituting the given values into the formula, we have:
![]()
Therefore, the frequency of the seismic wave is 100 Hz.
Problem 3:
A seismic wave with a velocity of 3000 m/s and a frequency of 50 Hz travels through a medium. Calculate the wavelength of the seismic wave.
Solution:
Using the formula for wave velocity:
![]()
we can rearrange the formula to solve for wavelength:
![]()
Substituting the given values into the formula, we have:
![]()
Therefore, the wavelength of the seismic wave is 60 m.
Also Read:
- How to measure velocity in magnetohydrodynamics
- How to find linear acceleration from angular velocity
- How to calculate velocity in nanophysics
- Escape velocity 2
- How to find orbital velocity of satellites
- Angular velocity formula
- How to find velocity with acceleration
- How to find velocity of an object
- How to find velocity with height and distance
- How to find translational velocity

The TechieScience Core SME Team is a group of experienced subject matter experts from diverse scientific and technical fields including Physics, Chemistry, Technology,Electronics & Electrical Engineering, Automotive, Mechanical Engineering. Our team collaborates to create high-quality, well-researched articles on a wide range of science and technology topics for the TechieScience.com website.
All Our Senior SME are having more than 7 Years of experience in the respective fields . They are either Working Industry Professionals or assocaited With different Universities. Refer Our Authors Page to get to know About our Core SMEs.
