CONTENTS
- What is Multiplexing ?
- What are the types of Multiplexing ?
- Time Division Multiplexing (TDM)
- Descriptions of TDM
- Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM)
- Descriptions of FDM
- TDM vs FDM
What is Multiplexing ?
Define Multiplexing:
“Multiplexing is a method where many message signs are assembled into a composite signal for the purpose of transmission through a communication channel”.
These signals are transmitted through one communication channel. The signals have to be specified so that they do not interfere with one another, and they have to be separated in the receiver end again to recreate the original signal.

Multiplexing Techniques
It is of two types as follows:
- Time Division Multiplexing (TDM)
- Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM)
Time Division Multiplexing:
What is TDM?
“Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) is a technique in which a number of signals are made to pass through a common channel at different time slots.“
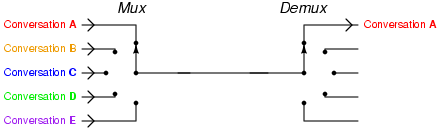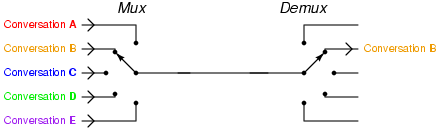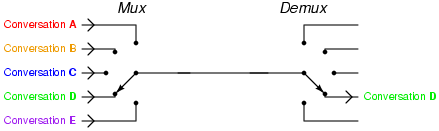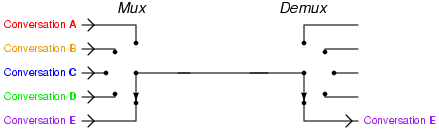
Image credit: Tony R. Kuphaldt, Telephony multiplexer system, CC BY 1.0
Diagram of TDM:

Here, the TDM technique is employed to the three analog resources that are multiplexed through a PCM system. In practice, a digital switch is utilized for its sampler. This fs = 1/Ts represents the frequency of spinning to its sampler; also fs fits the Nyquist rate for its analog sources with the maximum selective bandwidth. In the certain process where the bandwidth of these is different, the bigger bandwidth resources could be linked to many switch places onto the sampler side to be usually sampled more than the shorter bandwidth input signal.
In the receiver, the sampler needs to be connected with the processed waveform, so the PAM samples corresponding to input one will show up on the channel just only output signal. This is known as ‘frame synchronization’. Lpf has been utilized to rebuild the analogue signals in the PAM samples. ISI resulting in bad channel filtering may induce PCM samples from one communication channel to look on other station, and frame synchronization condition has been maintained. The feedthrough of a one specific communication channel into the other channel is known as cross-talk.
Advantages and Disadvantages of TDM:
Advantages of TDM
- Usually, TDM is more flexible than FDM.
- The circuit design of TDM is not complicated.
- In TDM, less cross-talk has occurred.
- Channel bandwidth length is longer.
Disadvantages of TDM
- Frequency Division Multiplexing process has no need of synchronization.
- Implementation can be complex.
Applications of TDM
- In ISDN (integrated service digital network), TDM is used.
- In PSTN (public switched telephone network), TDM is used.
- In a telephone system, TDM is widely used.
- TDM is used in telephone wire lines.
Frequency Division Multiplexing:
What is FDM?
“Frequency Division Multiplexing is a mechanism of signal transmission in which sharing the available bandwidth of a communication channel occurs among the signals to be transmitted.“
In general, FDM schemes are utilized for the analog signal applications.
Diagram of Frequency division Multiplexing:

FDM is a method of transmitting many messages concurrently through a wideband by modulating the message signals on a few subcarriers and forming a composite baseband signal. This mixed signal is dependent on the quantity of those controlled subcarriers. This mixed signal could then be modulated by AM, DSB, SSB, PM, FM, as the primary types. The type of modulation used in the subcarriers may differ, and also the type used in carrier signal could also differ.
On the other hand, the mixed signal range should consist of inputs signal that should not possess overlapping spectra; otherwise, cross-talk will happen involving the receiver end’s message signals. The mix baseband signal subsequently modulates the transmitter to create the FDM signal sent across the wideband channel.
This FDM collected and demodulated to recreate the combination baseband signal filtered through filters and modulated subcarriers. The sub-carrier has to be demodulated to reproduce the message signals such as m1(t), m2(t) etc.
A speaker with a traditional monaural FM receiver may listen to that the audio sound (composed of the remaining – and the right-channel sound ). By comparison, a speaker with a stereo recipient will get the left-channel sound on the left speaker and the right-channel sound on the ideal speaker. The gap sound is used to govern a 38-kHz DSB-SC sign. Even a 19-kHz pilot tone has been mixed into the mix baseband signal mb(t) to supply a reference sign for coherent subcarrier demodulation in receiver end. As we all know, this program can be used with present FM monaural recipients.
Advantages and Disadvantages of FDM:
Advantages of FDM
· Between the transmitter and receiver, unlike TDM, FDM does not need any synchronization.
· Through FDM, a large number of signals can be transmitted simultaneously.
· Slow, narrowband fading can only affect one single channel.
· Demodulation of FDM is much easier comparatively than TDM.
Disadvantages of FDM
- This suffers from cross-talk problem.
- In this type Communication channel must have a large bandwidth.
- In the technique, its channels get affected due to band fading.
- In FDM intermodulation distortion takes place.
Applications of FDM
- Frequency Division Multiplexing has applications in TV networks.
- FDM is used for FM & AM radio broadcasting.
- FDM was also being used in the first-generation cellular telephone.
For more electronics related article click here

Hi, I am Soumali Bhattacharya. I have done Master’s in Electronics.
I am currently invested in the field of Electronics and communication.
My articles are focused on the major areas of core electronics in a very simple yet informative approach.
I am a vivid learner and try to keep myself updated with all the latest technologies in the field of Electronics domains.
Let’s connect through LinkedIn –
