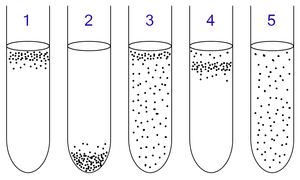
The obligate anaerobes are the microbes that are destroyed in by the normal concentration in the atmosphere of oxygen and its tolerance varies accordingly.
The very basic example for obligate anaerobes can be the bacteria that can live with no presence of oxygen. The tolerance of the obligate anaerobes can vary according to the species that are able to love in up to an oxygen level of 8% while the rest shall be viable to it.
They can be viable to the presence of oxygen having its concentration more than 0.5%. The growth of the bacteria being obligate anaerobes or obligate aerobes can be seen while getting them cultivated. The aerobes need up oxygen as they are not able to ferment or also respire anaerobically like the obligate anaerobes. They shall be able to gather more gas on the tube having the highest of it.
On the other hand, the obligate anaerobes are not good with oxygen. this gas tends to be hazard to the gas and thus they shall be seen gathering in the bottom of the cultured tube that has have least amount of the oxygen concentration. The other part except the obligate anaerobes and the obligate aerobes are the facultative ones that are able to grow with or even without the presence of oxygen.
The sensitivity of this obligate anaerobes towards the gas has also been linked with many factors that contains the production of enzymes and also oxidative stress. The oxygen can be tempting to destroy the obligate anaerobes as it cannot involve the oxidative stress in many ways as it has two electrons that are unpaired molecule of oxygen in the top of the o=molecular orbit being reduced to superoxide.
Along with obligate anaerobes getting it reduced to superoxide it also tends to come down to hydrogen peroxide inside the cells. A reaction in many ways in these products can be by making of the free hydroxyl radicals. The hydrogen peroxide and the superoxide that has been reduced by obligate anaerobes are the class of the compounds called as the reactive oxygen species. These are dangerous to the obligate anaerobes. In contrast, an aerobic organism is an organism that requires an oxygenated environment.
The obligate anaerobes tend to covert its nutrient to energy via the method of anaerobic respiration or also can use fermentation. In the aerobic ones, the pyruvate shall be made from glycolysis and is transferred to Acetyl-CoA. This is then broken to the TCA cycle and also in the electron transport chain. Anaerobic yields more energy than the aerobic and thus they tending to be called as facultative anaerobes and seen in the culture in the thoiglycolate broth. Anaerobes may be unicellular or multicellular.
The tending to be called so obligate anaerobes are seen in the place that is free of the gas oxygen and such places can be the still waters, deep in the ocean, the dep soil sediments, the landfills and the animal intestinal tracts. Some of the examples of the obligate anaerobes can be the Veillonella, the Actinomyces, the Clostridium, the Prevotella, Fusobacterium and some of the Rhodococcus, Mycobacterium.
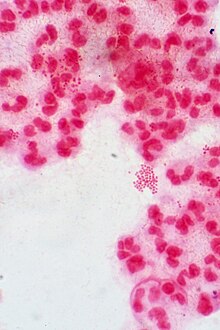
Veillonella
They are called to the gram negative type of bacteria that are obligate anaerobes that stain to pink like the anaerobic cocci.
These obligate anaerobes are called for its ability to have the lactate fermented. It is much of a normal bacterium in the oral mucosa and also of the intestine of the mammals. They also have been implicated in humans like for the Veillonella purvula.
These obligate anaerobes are the bacteria that reduced most of the nitrate in the oral cavity that is of much use as the anti-bacterial. The lactate is said to be fermented to propionate and also the acetate by the path of methylmalonyl-CoA method. Very less ATP is made in this way of fermentation. High of the substrate affinity is said to be the reason for this. The reaction for the obligate anaerobes 3 Lactate → acetate + 2 propionate + CO2+ H2O.
A study for this obligate anaerobes example has said that this bacterium in the athletes the endurance of it has been seen to be in good amount in the gut and is linked with having the treadmill increased its run time action. This effect shall be seen as the organism propionate the metabolite making from the lactic acid. They are the obligate anaerobes being anaerobic counterpart of the Neisseria.
Actinomyces
They are from the genus of Actinomycetia and are of the class for bacteria that are gram positive. They are also said to be gram positive.
This obligate anaerobes type belonging to the A.israelii and the A.meyeri are the obligate anaerobes with they grow good in the anaerobic ways. They can be seen to make endospores and also while some of these can be seen in a rod shape, its colony make fungus.
They are not exactly like fungus yet make branches like tm and the network made is called as hyphae. The aspect of it is mostly led by the wrong assumption that these obligate anaerobes are fungus and thus the name means ray fungus. The species of this type of obligate anaerobes are seen in soil and also in animals including the human. They are also unbiquitous and are called for viral role.
They are vital in soil ecology and also make many number of enzymes that shall help in degrading the organic matter of plant and also shall have chitin and lignin. Thus, the presence of this is vital in making of compost. Certain obligate anaerobes are seen in the vaginal, gut, oral and skin flora of the livestock and human. They also can cause bad report to the humans via wounds.
Actinomycetes is a nontaxonomic term for a group of common soil microorganisms sometimes called “thread or ray bacteria.” They are known for decomposing more resistant organic materials such as chitin, a complex sugar found in the outer skeleton of insects and elsewhere. Actinobacteria is a phylum of gram-positive bacteria with high G+C content. Among gram-positive bacteria, actinobacteria exhibit the richest morphological differentiation.
Clostridium
They are the gram positive ones and contains many other viral human pathogens that shall consist of the causing agents of tetanus and the botulism.
The gems of it that is mostly made is a vital reason for diarrhea. These are the obligate anaerobes that are able to make endospores with the normal spore of reproduction of it is called the vegetative mode and is rod shaped giving it a Greek name.
The spore of this obligate anaerobes is said to be thin and in shape of a bottle that helps in separate from the rest of the spores of bacteria that can be oval in shape. They are also the basic inhabitant in the soil and also in the animal tract also in humans. The normal place of its existence is the lower reproduction tract of the female being healthy. This obligate anaerobes genus has many species look same but are not alike.

These can include many pathogens and thus shall be able to cause much problems to the humans. The botulinum can make the toxin called as botulinum in wounds or the foods and thus cause botulism making these obligate anaerobes harmful. The same toxin also called as Botox is used in having cosmetic surgery that shall help paralyzing the face muscles and then reduce the aging sign and also help in many therapies.
The word anaerobic indicates “without oxygen.” The term has many uses in medicine. Anaerobic bacteria are germs that can survive and grow where there is no oxygen. For example, it can thrive in human tissue that is injured and does not have oxygen-rich blood flowing to it. Anaerobic metabolism is the creation of energy through the combustion of carbohydrates in the absence of oxygen.
Prevotella
These obligate anaerobes type are of the gram negative type. They are members of the vagina, gut, and the oral that seem to be mostly recovered.
The recovery for this is mostly from the infections that are anaerobic to the respiration tract. These causes shall contain the pneumonia, the lung affect, the sinusitis the heart empyema and chronic Otis. They tend to also burin the mouth area.
These obligate anaerobes are much common also to the vagina and via the increase of it in abundance shall cause vaginal mucosa that has been lined with bacterial vaginosis. It is also see to be most inherited by the group of bacteria that is vaginal microbiome and can also in abundance shall be connected with the mass of body and the hormonal milieu.

It gets in the way of making ammonia and also lipopolysaccharides that are itself a part of the mucosa in vagina. It is connected with the epithelial making of cytokine and also gives a boost to the growth of the rest of the vaginal bacteria linked microbes like the Gardnerella vaginalis. However, at last also stimulates its growth after. It is also called to be the obligate anaerobes that cause pigmentation.
Prevotella bivia produces lipopolysaccharides and ammonia that are part of vaginal mucus. It is also associated with epithelial cytokine production and enhances the growth of other bacterial vaginosis-associated organisms, such as Gardnerella vaginalis. Prevotella strains are Gram-negative, non-motile, rod-shaped, singular cells that thrive in anaerobic growth conditions.
Fusobacterium
They are the obligate anaerobes that are anaerobic and also gram negative in nature with no spore making and are same to that of the bactericides.
The cells that are individual to these obligate anaerobes are slender being a rod like bacilli that has pointed ends. The strains of this type of obligate anaerobes shall get the humans to face many problems like the Lemierre’s syndrome, the periodontal problem and also skin ulcer.
There are several sources that tells that this is a part of normal human flora called oropharynx and the recent consensus is this should always be considered to be a pathogen. It is also a gut linked commensal linked with the healthy people and called to be different obligate anaerobes. They tend to flourish in cells of the colon cancer and is also commonly linked with the ulcerative colitis with all the researchers not being sure of its part.
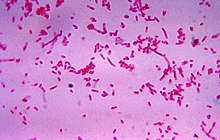
Fusobacterium is a Gram-negative non-spore forming bacterium that is widely known and studied as a human and animal pathogen. Fusobacterium’s exceptional ability to adhere with both Gram-negative and Gram-positive plaque microorganisms in biofilms has made it a highly invasive pathogen. Primarily given attention for its peridontal implications, strains of Fusobacterium have been identified as pathogen to many parts of the body.
fusobacterium can be responsible for periodontal disease, jugular vein suppurative thrombophlebitis, skin ulcers, intraabdominal abscesses, neck space infections, polymicrobial infections, and peritonsillar abscesses. Fusobacteriota are obligately anaerobic non-sporeforming Gram-negative bacilli. Since the first reports in the late nineteenth century, various names have been applied to these organisms.
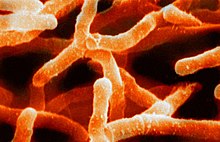
Rhodococcus
Rhodococcus has been greatly researched as a potential agent for the bioremediation of pollutants as it is commonly found in the natural environment and they possess certain characteristics.
Rhodococci also contain characteristics that enhances their ability to degrade organic pollutants. Their hydrophobic surface allows for adhesion to hydrocarbons, which enhances its ability to degrade these pollutants. They have a wide variety of catabolic pathways and many unique enzyme functions.

Rhodococci possess many properties that makes them suitable for bioremediation under a range of environments. Their ability to undergo microaerophilic respiration allows them to survive in environments containing low oxygen concentrations, and their ability to undergo aerobic respiration also allows them to survive in oxygenated environments. They also undergo nitrogen fixation, which allows them to generate their own nutrients in environments with low nutrients and they have the capability to metabolize many hydrocarbons.
These obligate anaerobes gives them the ability to degrade many recalcitrant, toxic hydrocarbons. Rhodococcus has also been identified as a contaminant of DNA extraction kit reagents and ultrapure water systems, which may lead to its erroneous appearance in microbiota or metagenomic datasets. Their hydrophobic surface allows for adhesion to hydrocarbons, which enhances its ability to degrade these pollutants. They have a wide variety of catabolic pathways and many unique enzyme functions
Mycobacterium
This genus includes pathogens known to cause serious diseases in mammals, including tuberculosis and leprosy in humans.
Mycobacterium is a genus of Actinomycetota, given its own family, the Mycobacteriaceae. Over 190 species are recognized in this genus. This genus includes pathogens known to cause serious diseases in mammals, including tuberculosis.
Acid fast stains are used to differentiate acid fast organisms such mycobacteria. Acid fast bacteria have a high content of mycolic acids in their cell walls. Acid fast bacteria will be red, while nonacid fast bacteria will stain blue/green with the counterstain with the Kinyoun stain. The cell walls of mycobacteria are very thick and consist of four layers. The innermost layer is composed of peptidoglycan and the others of lipids. The latter are ubiquitous in the environment and occur in soil and water; some of them are present in the gastrointestinal tract of some humans and animals.

The cell wall composition renders mycobacteria hydrophobic, and as a result these bacteria tend to grow in aggregates that ‘float’ on the surface of liquid media, which need to be combined with phenol to allow penetration of the cell wall. The presence of lipid provides the bacteria with resistance to acid and alkaline environments and renders the cells relatively impermeable to various basic dyes. The genus Mycobacterium includes acid-fast bacteria that are known pathogens, along with numerous saprophytes.
Also Read:
- Does splicing occur in prokaryotes
- Dental anatomy
- Do eukaryotes have introns
- Protists cell walls and bacteria cell walls
- Cytoplasm in white blood cell
- Are proteins polymers
- Anabolic enzyme example
- Examples of endoparasites
- Cytoplasm and protoplasm
- Holoenzyme and apoenzyme
I am Ankita Chattopadhyay from Kharagpur. I have completed my B. Tech in Biotechnology from Amity University Kolkata. I am a Subject Matter Expert in Biotechnology. I have been keen in writing articles and also interested in Literature with having my writing published in a Biotech website and a book respectively. Along with these, I am also a Hodophile, a Cinephile and a foodie.

Hi Fellow Reader,
We're a small team at Techiescience, working hard among the big players. If you like what you see, please share our content on social media. Your support makes a big difference. Thank you!