Introduction:
Polarization is a term used to describe the division or separation of people or groups into opposing factions or beliefs. It refers to the process by which individuals or communities develop extreme and contrasting views on a particular issue, often leading to a lack of understanding and communication between different sides. In today’s society, polarization has become increasingly prevalent, particularly in the realms of politics, social issues, and even everyday conversations. It can be seen as a result of various factors, such as media influence, ideological differences, and the echo chamber effect. Understanding polarization is crucial in order to bridge the gaps between different perspectives and foster constructive dialogue.
Key Takeaways:
| Polarization | Definition |
|---|---|
| Description | Division or separation of people or groups into opposing factions or beliefs |
| Causes | Media influence, ideological differences, echo chamber effect |
| Impact | Lack of understanding and communication, hindered constructive dialogue |
| Relevance | Prevalent in politics, social issues, and everyday conversations |
Understanding the Concept of Polarization
Definition of Polarization
Polarization is a term used to describe the division or separation of individuals or groups into opposing or distinct ideological, political, social, or cultural beliefs and values. It refers to the process by which people become more extreme in their opinions and attitudes, leading to a widening gap between different perspectives. This phenomenon can be observed in various aspects of society, including politics, media, public opinion, communication, culture, technology, economics, and even religion.
The Origin of the Term “Polarization”
The term “polarization” finds its roots in the field of physics, where it refers to the alignment of electromagnetic waves in a specific direction. In the context of social sciences, the concept of polarization was first introduced to describe the division of public opinion and political ideologies. Over time, it has become a widely used term to depict the increasing divide between individuals or groups with differing beliefs and values.
Polarization in Politics:
In the realm of politics, polarization occurs when political parties and their supporters become more ideologically rigid, leading to a sharp divide between left-wing and right-wing ideologies. This can hinder effective governance and compromise, as politicians become less willing to find common ground and work towards bipartisan solutions.
Polarization in Society:
Social polarization refers to the division of society along various lines, such as income inequality, racial or ethnic differences, and cultural values. It can lead to social unrest, discrimination, and a lack of social cohesion, as individuals and groups become more segregated and less willing to understand and empathize with one another.
Polarization in Media:
Media polarization occurs when news outlets and media platforms present information in a biased or one-sided manner, catering to specific ideological or partisan audiences. This can contribute to the formation of echo chambers, where individuals are exposed only to information that aligns with their existing beliefs, further reinforcing polarization.
Polarization in Public Opinion:
Public opinion polarization refers to the increasing divergence of attitudes and beliefs among the general public on various issues. This can be influenced by factors such as political rhetoric, media framing, and social media algorithms, which often amplify extreme viewpoints and contribute to the polarization of public discourse.
Polarization in Communication:
In the realm of communication, polarization can be observed in the way people engage with one another. It often leads to a breakdown in civil discourse, as individuals become less willing to listen to opposing viewpoints and more inclined to engage in heated debates or personal attacks.
Polarization in Culture:
Cultural polarization occurs when different cultural groups develop distinct and often conflicting values, norms, and practices. This can lead to cultural clashes, intolerance, and a lack of cultural understanding and appreciation.
Polarization in Technology:
Technological advancements have also contributed to polarization, as algorithms and social media platforms often prioritize content that aligns with users’ preferences and beliefs. This can create filter bubbles, where individuals are exposed only to information that reinforces their existing views, further deepening polarization.
Polarization in Economics:
Economic polarization refers to the increasing gap between the rich and the poor, as well as the shrinking middle class. This can lead to social and economic inequality, as well as political and social unrest.
Polarization in Religion:
Religious polarization occurs when different religious groups become more rigid in their beliefs and less tolerant of other faiths. This can lead to religious conflicts, discrimination, and a lack of religious pluralism.
In conclusion, polarization is a complex and multifaceted concept that permeates various aspects of society. It is essential to understand and address the causes and consequences of polarization in order to foster greater understanding, empathy, and cooperation among individuals and groups with differing beliefs and values.
Polarization in Different Fields
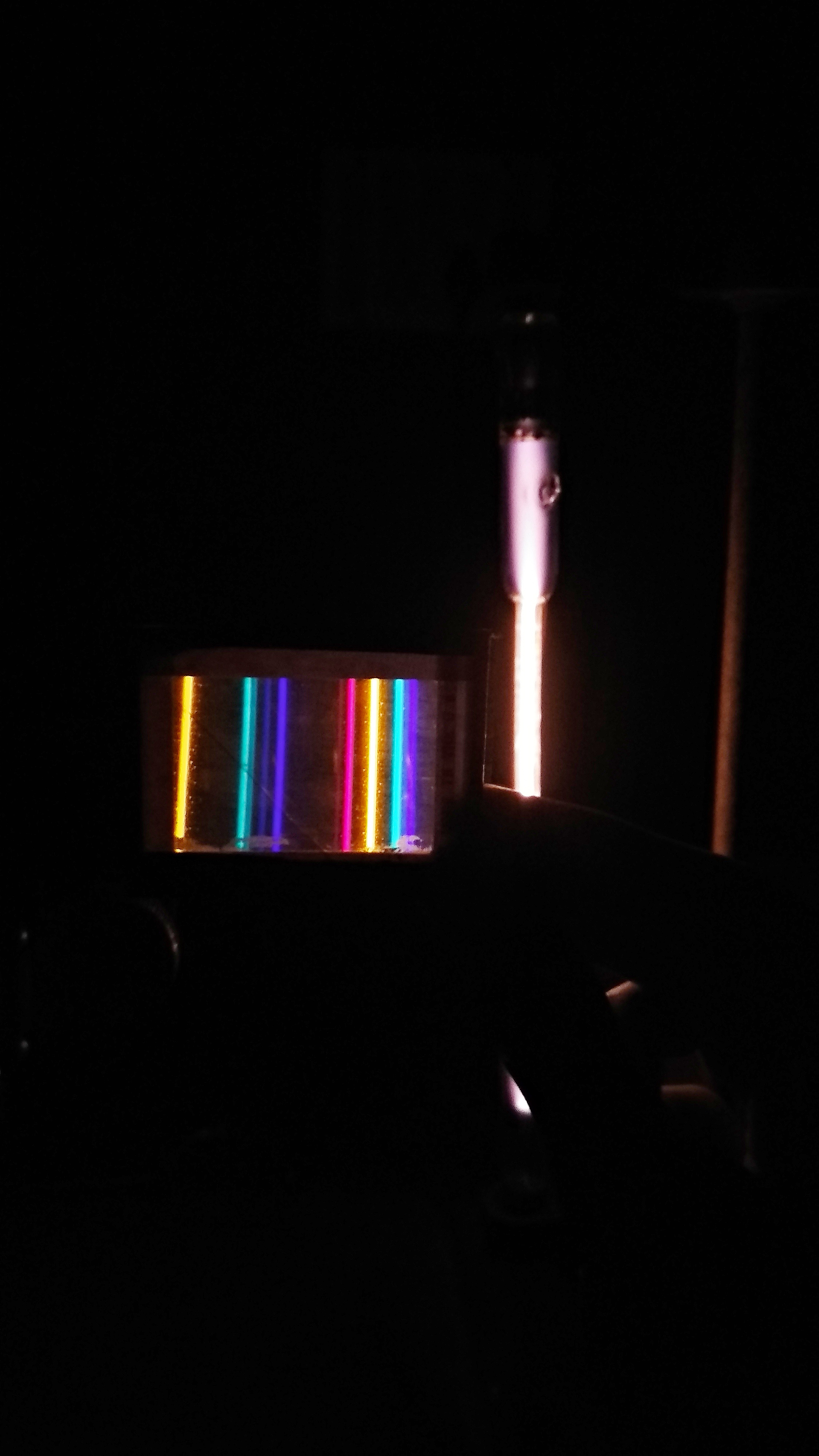

Polarization in Physics
In the field of physics, polarization refers to the orientation of the electric field vector of an electromagnetic wave. It is a fundamental concept that plays a crucial role in understanding the behavior of light and other electromagnetic waves. Polarization can be described as the direction in which the electric field oscillates as the wave propagates through space.
There are different types of polarization, including linear polarization, circular polarization, and elliptical polarization. Linear polarization occurs when the electric field oscillates in a single plane, while circular polarization occurs when the electric field rotates in a circular motion. Elliptical polarization is a combination of linear and circular polarization.
Polarization in physics has applications in various areas, such as optics, telecommunications, and quantum mechanics. It is used in technologies like polarized sunglasses, optical filters, and liquid crystal displays (LCDs). Understanding polarization is essential for engineers and scientists working in these fields.
Polarization in Chemistry
In the field of chemistry, polarization refers to the distortion of electron density within a molecule or an atom. It occurs when there is an uneven distribution of electrons, leading to the development of partial positive and negative charges. This phenomenon is crucial in understanding chemical bonding and molecular interactions.
Polarization in chemistry can be classified into two types: electronic polarization and molecular polarization. Electronic polarization occurs when the electron cloud of an atom or molecule is distorted due to the presence of an electric field. Molecular polarization, on the other hand, refers to the distortion of electron density within a molecule caused by the presence of nearby atoms or molecules.
The concept of polarization in chemistry is fundamental to understanding various chemical phenomena, such as solubility, intermolecular forces, and reaction mechanisms. It plays a significant role in fields like organic chemistry, physical chemistry, and materials science.
Polarization in Electrical Engineering
In the field of electrical engineering, polarization refers to the separation of positive and negative charges within a material or an electrical system. It is a crucial concept in understanding the behavior of electrical circuits and devices.
Polarization in electrical engineering can be categorized into several types, including dielectric polarization, electrode polarization, and interface polarization. Dielectric polarization occurs when an electric field causes the alignment of polar molecules within a dielectric material. Electrode polarization, on the other hand, refers to the accumulation of charges at the electrode-electrolyte interface in an electrochemical system. Interface polarization occurs at the boundary between two different materials with different electrical properties.
Understanding polarization in electrical engineering is essential for designing and analyzing electrical circuits, power systems, and electronic devices. It is used in various applications, such as capacitors, batteries, and sensors.
Overall, polarization is a concept that finds its relevance in various fields, including physics, chemistry, and electrical engineering. It provides a deeper understanding of the behavior of light, chemical bonding, and electrical systems. By grasping the concept of polarization, we can gain insights into the intricate workings of the natural world and the technologies that shape our lives.
Keywords: polarization, meaning, definition, concept, understanding, political, social, divide, division, ideological, polarization, polarization in politics, polarization in society, polarization in media, polarization in public opinion, polarization in communication, polarization in culture, polarization in technology, polarization in economics, polarization in religion.
Polarization in Politics
Definition of Political Polarization
Political polarization refers to the increasing divide between individuals or groups with opposing political beliefs and ideologies. It is a concept that has gained significant attention in recent years, as societies around the world have become more divided along ideological lines.
What Does Partisan Polarization Mean?
Partisan polarization specifically refers to the division between political parties and their supporters. It occurs when individuals align themselves strongly with one political party and view the opposing party as a threat or enemy. This type of polarization often leads to a lack of cooperation and compromise between parties, making it difficult to find common ground on important issues.
Examples of Polarization in Politics
Polarization in politics can be observed in various aspects of society, including media, public opinion, communication, culture, technology, economics, and even religion. Here are some examples:
Media: The media plays a crucial role in shaping public opinion and can contribute to polarization. News outlets with different political leanings often present biased information, reinforcing existing beliefs and creating an “us versus them” mentality.
Public Opinion: Polarization can be seen in the way people form their opinions on political matters. Individuals tend to seek out information that aligns with their pre-existing beliefs, leading to confirmation bias and further division.
Communication: Polarization affects the way people communicate with each other. Instead of engaging in constructive dialogue, individuals may resort to personal attacks and dismiss opposing viewpoints, hindering productive discussions.
Culture: Cultural polarization occurs when certain cultural values and beliefs become associated with specific political ideologies. This can lead to a sense of “cultural warfare” and further deepen the divide between different groups.
Technology: Social media platforms and online echo chambers can contribute to political polarization. Algorithms often show users content that aligns with their preferences, creating filter bubbles and limiting exposure to diverse perspectives.
Economics: Economic policies and inequality can also contribute to polarization. Disagreements over issues such as taxation, welfare, and income distribution can create divisions between different socioeconomic groups.
Religion: Religious polarization occurs when religious beliefs become intertwined with political ideologies. This can lead to conflicts and divisions within societies, as different religious groups may hold opposing views on social and political issues.
Overall, polarization in politics has significant implications for democratic processes and societal cohesion. It is important to foster understanding and bridge the divide between different ideological groups to promote a more inclusive and harmonious society.
The Impact of Polarization
Polarization refers to the division or separation of individuals or groups into opposing factions or ideologies. It has far-reaching effects on various aspects of society, including politics, social dynamics, communication, culture, technology, economics, and even religion. Let’s explore the effects of polarization in society and its role in war and conflict.
The Effects of Polarization in Society
Polarization in society can have both positive and negative effects. On one hand, it can foster healthy debates, encourage critical thinking, and lead to the development of diverse perspectives. This can contribute to a vibrant democracy and the exploration of innovative ideas.
However, when polarization becomes extreme, it can lead to detrimental consequences. Here are some effects of polarization in society:
Increased Divisions: Polarization often creates deep divisions within society, as people align themselves with specific ideologies or beliefs. This can lead to a breakdown in communication and understanding between different groups.
Erosion of Trust: Polarization can erode trust in institutions, such as the government, media, and even scientific consensus. When people are deeply divided, they may question the motives and credibility of those who hold opposing views.
Echo Chambers: Polarization can result in the formation of echo chambers, where individuals only engage with like-minded people and consume information that reinforces their existing beliefs. This can further entrench divisions and hinder the exchange of diverse perspectives.
Political Gridlock: In highly polarized political environments, it becomes challenging to find common ground and reach consensus on important issues. This can lead to political gridlock, where progress is stalled, and societal problems remain unresolved.
Social Fragmentation: Polarization can fragment society along ideological lines, leading to social isolation and the breakdown of social cohesion. This can have negative consequences for community engagement, cooperation, and collective action.
The Role of Polarization in War and Conflict
Polarization plays a significant role in fueling and exacerbating conflicts, both domestically and internationally. Here are some ways in which polarization influences war and conflict:
Identity Politics: Polarization often taps into people’s sense of identity, whether it be based on ethnicity, religion, or nationality. This can lead to the manipulation of identity politics, where groups are pitted against each other, resulting in heightened tensions and the potential for violent conflict.
Us vs. Them Mentality: Polarization fosters an “us vs. them” mentality, where individuals or groups perceive those with opposing views as enemies or threats. This mindset can escalate conflicts and make peaceful resolutions more challenging to achieve.
Propaganda and Misinformation: Polarized environments are fertile ground for the spread of propaganda and misinformation. Manipulative actors can exploit divisions to disseminate false narratives, further deepening the divide and inflaming conflicts.
Radicalization: Extreme polarization can contribute to the radicalization of individuals or groups. When people feel marginalized or threatened, they may resort to violence as a means to defend their beliefs or advance their agenda.
International Relations: Polarization within and between nations can have ripple effects on international relations. Ideological divisions can hinder diplomatic efforts, escalate tensions, and even lead to military confrontations.
In conclusion, polarization has a profound impact on society, influencing various aspects of our lives. While it can stimulate healthy debates and diverse perspectives, extreme polarization can lead to divisions, erosion of trust, and even violent conflicts. It is crucial to foster open dialogue, empathy, and understanding to mitigate the negative effects of polarization and promote a more cohesive and peaceful society.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the term “polarization” refers to the division or separation of people into opposing groups or factions, often characterized by extreme differences in beliefs, opinions, or ideologies. It is a phenomenon that can be observed in various aspects of society, including politics, religion, and social issues. Polarization can lead to a breakdown in communication and understanding between individuals or groups, as well as the formation of echo chambers where people only interact with those who share similar views. Understanding polarization is crucial in fostering dialogue, empathy, and finding common ground to bridge the gaps between different perspectives.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does polarization mean?
Polarization refers to the process or state of dividing or grouping people, ideas, or opinions into two contrasting or opposing groups.
What does the term polarity mean?
The term polarity refers to the condition of having two opposite or contrasting aspects, ideas, or opinions.
What does polarization mean in politics?
Political polarization refers to the division or separation of individuals or groups into distinct ideological or partisan factions, often resulting in increased hostility and decreased cooperation.
What does polarization mean in society?
Social polarization refers to the division or segregation of society into distinct groups based on factors such as income, education, or political beliefs, leading to increased social inequality and fragmentation.
What does polarization mean in media?
Media polarization refers to the tendency of media outlets to present news and information in a way that aligns with a particular ideological or partisan perspective, often leading to the reinforcement of existing beliefs and the creation of echo chambers.
What does polarization mean in public opinion?
Public opinion polarization refers to the increasing divergence of opinions and attitudes among the general public on various issues, often resulting in a more polarized and divided society.
What does polarization mean in communication?
Polarization in communication refers to the phenomenon where individuals or groups selectively engage with information or media that aligns with their existing beliefs, leading to the reinforcement of those beliefs and a lack of exposure to alternative perspectives.
What does polarization mean in culture?
Cultural polarization refers to the division or separation of society into distinct cultural groups with differing values, beliefs, or practices, often leading to increased cultural clashes and conflicts.
What does polarization mean in technology?
Technological polarization refers to the unequal distribution or access to technology, resulting in a digital divide between those who have access to advanced technology and those who do not, exacerbating existing social and economic inequalities.
What does polarization mean in economics?
Economic polarization refers to the increasing gap between the rich and the poor, resulting in a society with extreme wealth inequality and limited social mobility.
Also Read:
- Spherical aberration
- Mirror reflection examples
- Psychrometer hygrometer humidity dew point
- Convection vs diffusion
- Mercury formation structure and facts
- Micrometer read micrometer types important facts
- How to find static equilibrium
- Is magnetism a physical property
- Stable equilibrium example
- How to calculate kinetic friction

The TechieScience Core SME Team is a group of experienced subject matter experts from diverse scientific and technical fields including Physics, Chemistry, Technology,Electronics & Electrical Engineering, Automotive, Mechanical Engineering. Our team collaborates to create high-quality, well-researched articles on a wide range of science and technology topics for the TechieScience.com website.
All Our Senior SME are having more than 7 Years of experience in the respective fields . They are either Working Industry Professionals or assocaited With different Universities. Refer Our Authors Page to get to know About our Core SMEs.
