The process of zygote formation is a crucial step in sexual reproduction. When a sperm cell fertilizes an egg cell, they combine their genetic material to form a zygote. This fusion of genetic material from both parents creates a unique combination of genes that will determine the characteristics of the offspring. The zygote then undergoes cell division and development to eventually form an embryo.
Key Takeaways
| Fact | Information |
|---|---|
| Definition | Fusion of sperm and egg to form a zygote |
| Genetic material | Combination of genes from both parents |
| Importance | Determines characteristics of the offspring |
| Development | Zygote undergoes cell division and forms an embryo |
Understanding Zygote Formation

Zygote formation is a crucial process in human reproduction that occurs during fertilization. It involves the fusion of an egg cell (ovum) and a sperm cell, resulting in the formation of a new individual. This process marks the beginning of embryonic development and plays a vital role in genetic inheritance and the creation of genetic variation.
Definition of Zygote Formation
Zygote formation, also known as conception, is the process by which a haploid egg cell and a haploid sperm cell fuse together to form a diploid zygote. This fusion occurs during sexual reproduction and is the first step towards the development of a new organism. The zygote contains the complete set of genetic material, including DNA, from both parents.
During zygote formation, the male and female gametes come together, bringing their respective genetic information. The sperm cell carries genetic material in the form of chromosomes, while the egg cell contributes its own set of chromosomes. When these gametes fuse, the chromosomal combination creates a unique genetic makeup for the zygote.
Importance of Zygote Formation
Zygote formation is of utmost importance in reproductive biology as it initiates the process of embryogenesis. After fertilization, the zygote undergoes rapid cell division through mitosis, leading to the formation of an embryo. This early stage of prenatal development is crucial for the proper growth and differentiation of cells.
The zygote serves as the foundation for the development of a new individual. As it divides and differentiates, it forms a blastocyst, which implants itself into the uterine wall. From there, the embryo continues to grow and develop, eventually leading to the formation of various tissues, organs, and systems.
One significant aspect of zygote formation is the introduction of genetic variation. Through the fusion of gametes, the zygote inherits genetic material from both parents, resulting in a unique combination of traits. This genetic variation is essential for the survival and adaptation of species, as it allows for diversity within populations.
In summary, zygote formation is a critical step in human reproduction. It involves the fusion of an egg cell and a sperm cell, leading to the formation of a diploid zygote. This process initiates embryonic development and contributes to genetic inheritance and variation. Understanding the intricacies of zygote formation is fundamental to comprehending the complexities of human life and reproduction.
The Process of Zygote Formation
Zygote formation is a crucial step in the process of human reproduction. It occurs when the egg cell, also known as the ovum, is fertilized by a sperm cell. This process marks the beginning of embryogenesis, where the genetic material from both parents combines to form a new individual.
Steps in Zygote Formation
The process of zygote formation involves several steps that are essential for the successful development of an embryo. Let’s take a closer look at each of these steps:
Gametes Fusion: The first step in zygote formation is the fusion of the male and female gametes. The sperm cell, carrying genetic material from the father, penetrates the protective layers surrounding the egg cell. Once inside, the genetic material of the sperm combines with that of the egg, resulting in a chromosomal combination.
Cell Division: After fertilization, the zygote undergoes rapid cell division through a process called mitosis. This division allows the zygote to grow and develop into an embryo. During mitosis, the genetic material is replicated, ensuring that each new cell receives a complete set of DNA.
Embryonic Stage: As the zygote continues to divide, it progresses through different stages of development. At the blastocyst stage, the embryo consists of a hollow ball of cells. These cells will later differentiate into different tissues and organs, laying the foundation for the development of a new individual.
Genetic Variation: Zygote formation plays a crucial role in genetic variation. Through the process of meiosis, the egg and sperm cells undergo a reduction in their genetic material, resulting in haploid cells. When these haploid cells fuse during fertilization, they create a diploid zygote with a unique combination of genetic material from both parents. This genetic variation contributes to the diversity seen in human populations.
Time Required for Zygote Formation
The time required for zygote formation can vary depending on various factors. After sexual reproduction, the sperm cell needs to reach the egg cell within a specific timeframe for fertilization to occur. Once fertilization takes place, the zygote begins its journey towards the uterus, where it will implant and continue its development.
On average, it takes around 24 to 48 hours for the sperm to reach the egg after sexual intercourse. After fertilization, the zygote undergoes several cell divisions and reaches the blastocyst stage within approximately 4 to 5 days. The blastocyst then implants into the uterine lining, marking the beginning of prenatal development.
In conclusion, zygote formation is a complex process that involves the fusion of male and female gametes, followed by cell division and embryonic development. This process is essential for genetic inheritance and the creation of a new individual. Understanding the steps and time required for zygote formation provides valuable insights into the fascinating world of reproductive biology.
Zygote Formation in Different Organisms

Zygote Formation in Humans
Zygote formation in humans is a crucial step in the process of human reproduction. It occurs when the egg cell, also known as the ovum, is fertilized by a sperm cell. This fertilization process leads to the fusion of the genetic material from both the male and female gametes, resulting in the formation of a diploid zygote.
During sexual reproduction, the male gamete, or sperm cell, fertilizes the female gamete, or egg cell, through the process of conception. This fusion of gametes brings together the genetic material, including the DNA, from both parents. The zygote then undergoes a series of cell divisions, known as mitosis, leading to the development of an embryo.
Embryogenesis, the process of embryonic development, involves cellular differentiation, where the cells of the zygote specialize and take on specific functions. As the embryo develops, it progresses through different stages, such as the blastocyst stage, before further cellular differentiation occurs. This process ultimately leads to the formation of different tissues and organs during prenatal development.
Zygote formation in humans is essential for genetic inheritance and the creation of genetic variation. Through the combination of chromosomal material from both parents, the zygote carries a unique set of genetic information. This genetic variation plays a crucial role in the diversity of human populations.
Zygote Formation in Plants
In plants, zygote formation also occurs through the process of sexual reproduction. The male gametes, contained within pollen grains, fertilize the female gametes, located within the ovules. This fertilization process leads to the formation of a diploid zygote.
Unlike in humans, where the zygote develops into an embryo, in plants, the zygote develops into a multicellular structure called the embryo sac. This embryo sac further develops into the embryo, which eventually gives rise to a new plant.
Plant zygote formation is essential for the propagation and continuation of plant species. It allows for the genetic inheritance and variation necessary for the adaptation and survival of plants in different environments.
Zygote Formation in Protists
Protists, a diverse group of eukaryotic microorganisms, also undergo zygote formation as part of their reproductive process. The specific mechanisms of zygote formation in protists can vary depending on the species.
In some protists, zygote formation occurs through the fusion of two haploid cells, resulting in the formation of a diploid zygote. This fusion of gametes brings together genetic material from two different individuals, contributing to genetic variation within the protist population.
Zygote formation in protists is an essential aspect of their life cycle and reproductive biology. It allows for the continuation of the species and the generation of genetic diversity, which can be advantageous for their survival in various environments.
Overall, zygote formation plays a critical role in the reproductive processes of different organisms, including humans, plants, and protists. It is a fundamental step in the development of new individuals and the transmission of genetic information from one generation to the next.
Post Fertilization Events
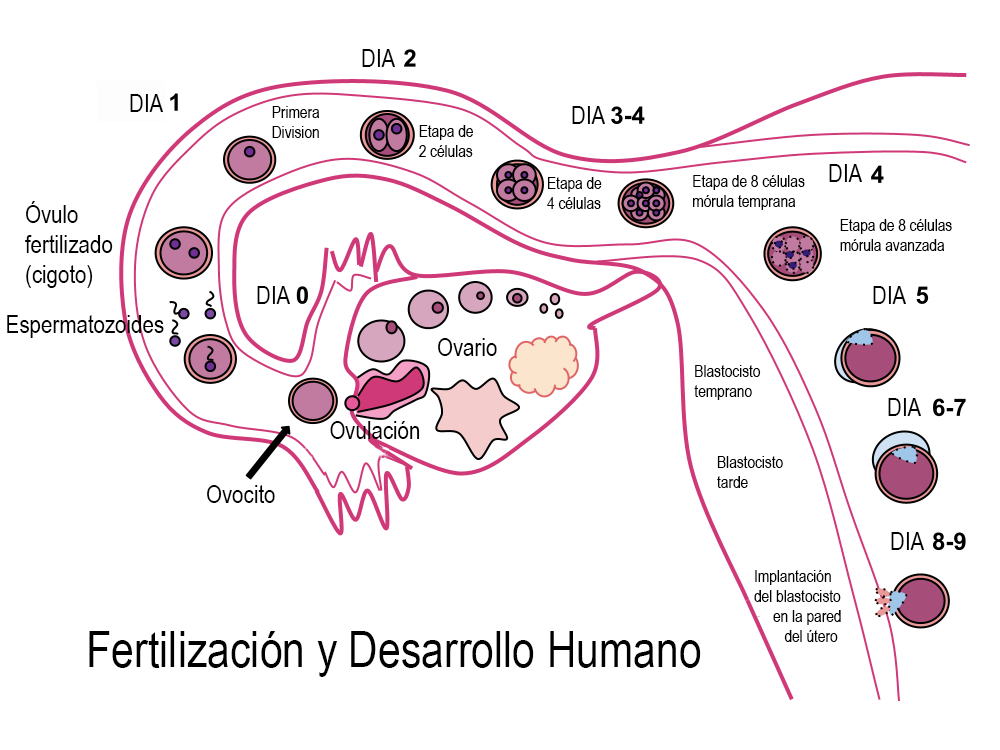
After the fertilization process, a series of events take place to ensure the successful development of the embryo. These events are collectively known as post-fertilization events. Let’s explore two important aspects of post-fertilization events: “Is Zygote Formation a Post Fertilization Event?” and “What Happens After Zygote Formation?”
Is Zygote Formation a Post Fertilization Event?
Yes, zygote formation is indeed a post-fertilization event. The zygote is formed when the sperm cell fertilizes the egg cell during the process of fertilization. This marks the beginning of the development of a new individual in sexual reproduction, such as in human reproduction.
The fusion of the genetic material from the sperm and the egg, which contains the DNA, results in the formation of a zygote. This genetic combination brings together the unique characteristics of both parents, contributing to genetic variation in offspring. The zygote is a diploid cell, meaning it contains two sets of chromosomes, one from each parent.
What Happens After Zygote Formation?
After the zygote is formed, a series of events occur to support the development of the embryo. These events involve cell division, cellular differentiation, and the formation of specialized structures.
Cell Division: The zygote undergoes rapid cell division through the process of mitosis. This division results in the formation of a cluster of cells called the blastocyst. The blastocyst consists of an outer layer of cells and an inner cell mass.
Cellular Differentiation: The cells within the blastocyst start to differentiate, meaning they take on specific roles and form different types of tissues. This process is crucial for the development of various organs and structures in the body.
Embryonic Stage: During the embryonic stage, which lasts for about eight weeks, the embryo undergoes significant growth and development. The cells continue to divide and differentiate, forming the foundation for the development of organs, limbs, and other structures.
Prenatal Development: As the embryo develops, it goes through different stages of prenatal development. These stages include the germinal stage, embryonic stage, and fetal stage. Each stage is characterized by specific milestones and changes in the developing organism.
Throughout these post-fertilization events, the genetic inheritance from both parents plays a crucial role in shaping the characteristics of the developing individual. The combination of genetic material from the male and female gametes contributes to the unique traits and genetic variation observed in offspring.
In summary, post-fertilization events, including zygote formation, cell division, cellular differentiation, and embryonic development, are essential for the successful progression of prenatal development. These events lay the foundation for the growth and formation of a new individual, ensuring the continuation of life through sexual reproduction.
Zygote Formation and Embryo Development
The process of zygote formation and embryo development is a crucial stage in human reproduction. It involves the fusion of an egg cell and a sperm cell, resulting in the formation of a zygote. This zygote then undergoes a series of developmental stages to eventually form an embryo.
Development of an Embryo from the Zygote
Once fertilization occurs, the genetic material from the egg cell and the sperm cell combines, resulting in the formation of a zygote. The zygote contains the complete set of DNA required for the development of a new individual. It is through the process of cell division, specifically mitosis, that the zygote begins to divide and multiply.
During embryogenesis, the zygote undergoes multiple rounds of cell division, known as cleavage. These divisions result in the formation of a blastocyst, which is a hollow ball of cells. The blastocyst then undergoes cellular differentiation, where the cells start to specialize and take on specific functions.
As the embryo continues to develop, it goes through various stages, including the embryonic stage. During this stage, the embryo undergoes further cellular differentiation and begins to develop the basic structures and organs of the body. This stage is crucial for the formation of the nervous system, cardiovascular system, and other vital organs.
Symptoms of Zygote Formation and Embryo Development
During the early stages of zygote formation and embryo development, there are typically no noticeable symptoms. However, as the embryo grows and develops, certain signs may indicate the progression of pregnancy.
One of the most common symptoms is a missed period, which is often the first indication of pregnancy. Other symptoms may include breast tenderness, fatigue, nausea, and frequent urination. These symptoms are a result of hormonal changes in the body and can vary from person to person.
It is important to note that not all individuals will experience the same symptoms, and some may not experience any symptoms at all. Additionally, these symptoms can also be associated with other conditions, so it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis.
In conclusion, zygote formation and embryo development are fundamental processes in human reproduction. The fusion of male and female gametes results in the formation of a zygote, which then undergoes a series of developmental stages to form an embryo. Understanding these processes is crucial for studying reproductive biology, genetic inheritance, and prenatal development.
Common Questions About Zygote Formation
Where Does Zygote Formation Take Place?
Zygote formation, also known as fertilization, is a crucial step in the process of human reproduction. It occurs when the egg cell, or ovum, and the sperm cell, or spermatozoon, fuse together to form a zygote. But where does this remarkable event take place?
Zygote formation takes place in the female reproductive system. Specifically, it occurs in the fallopian tubes, which are located on either side of the uterus. After ovulation, the egg cell is released from the ovary and travels through the fallopian tube. If fertilization occurs, it happens within the fallopian tube before the zygote continues its journey towards the uterus.
Is Zygote Formation Asexual?
No, zygote formation is not asexual. It is a result of sexual reproduction, which involves the fusion of male and female gametes. During sexual reproduction, the sperm cell and the egg cell, both containing half the genetic material (DNA) of the parent, come together to form a zygote.
The process of zygote formation involves the fusion of the haploid sperm cell and the haploid egg cell, resulting in the formation of a diploid zygote. This diploid zygote contains the complete set of genetic material necessary for the development of a new individual.
Zygote formation is a complex process that involves various stages, including cell division, mitosis, and meiosis. After fertilization, the zygote undergoes a series of divisions, leading to embryogenesis. These divisions eventually give rise to a blastocyst, which implants itself into the uterine wall and begins the process of cellular differentiation and prenatal development.
One of the significant advantages of sexual reproduction and zygote formation is the genetic variation it brings. The combination of genetic material from both parents leads to offspring with unique characteristics and traits. This genetic variation is essential for the survival and adaptation of species.
In summary, zygote formation takes place in the fallopian tubes of the female reproductive system. It is a result of sexual reproduction, involving the fusion of male and female gametes. This process leads to the formation of a diploid zygote, which undergoes further development and cellular differentiation to eventually form an embryo. Zygote formation plays a crucial role in genetic inheritance and the creation of genetic variation in offspring.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the formation of a zygote is a crucial step in the process of sexual reproduction. It occurs when a sperm cell fertilizes an egg cell, resulting in the fusion of their genetic material. This fusion creates a unique combination of genes that will determine the characteristics of the offspring. The zygote then undergoes rapid cell division and development to eventually form an embryo. The formation of a zygote marks the beginning of a new life and is the foundation for the growth and development of all living organisms. Understanding the process of zygote formation is essential in the field of biology and reproductive medicine.
What is the difference between zygote formation and embryo development?
The difference between zygote and embryo lies in their developmental stages. A zygote is formed when a sperm and an egg fuse during fertilization, marking the beginning of a new individual. On the other hand, an embryo is an early stage of development after the zygote has undergone cell division several times and has implanted into the uterine lining. While both zygote formation and embryo development are crucial stages in the reproductive process, the key distinction lies in the progression from a single fertilized cell (zygote) to a multi-cellular organism (embryo).
Frequently Asked Questions
How to do zygote formation?
Zygote formation, also known as fertilization, happens when a sperm cell from a male fuses with an egg cell from a female. This process combines the genetic material from both parents to create a diploid zygote, the first cell of a new organism.
What is zygote formation in humans?
In humans, zygote formation occurs when a sperm cell penetrates the ovum (egg cell) during conception. The genetic material of the sperm and egg merge, leading to the formation of a zygote, which contains a complete set of chromosomes from both parents.
What produces a zygote?
A zygote is produced by the fusion of male and female gametes (sperm and egg cells) during the process of fertilization. This fusion results in a single cell with a complete set of chromosomes, which will then undergo cell division to form an embryo.
How does zygote formation work in protists?
In protists, zygote formation occurs through sexual reproduction. Male and female gametes, produced through meiosis, combine to form a zygote. This zygote then undergoes mitosis, dividing into multiple cells, which eventually form a new protist.
Is zygote formation a post-fertilization event?
No, zygote formation is not a post-fertilization event. It is the result of fertilization itself. When a sperm cell fuses with an egg cell, their genetic material combines to form a zygote.
How long does it take for a zygote to form?
The formation of a zygote is an almost immediate process after the sperm successfully penetrates the egg. However, it takes about 24 hours for the combined genetic material to fully merge and start dividing, marking the beginning of embryogenesis.
What happens after zygote formation?
After zygote formation, the cell begins to divide through a process called mitosis, forming a multicellular embryo. This process continues, with cells differentiating into specialized types to form different tissues and organs, eventually resulting in a fully formed organism.
Why is zygote formation important?
Zygote formation is crucial in sexual reproduction as it leads to the creation of a new organism with genetic variation. This variation is important for the survival and evolution of species, as it increases the chances of adaptability to changing environments.
Where does zygote formation take place?
In humans and many animals, zygote formation takes place in the fallopian tubes of the female reproductive system. In plants, it occurs within the ovule after the pollen grain delivers sperm to the egg.
How to stop zygote formation?
Zygote formation can be prevented by various methods of contraception, which may prevent ovulation, block the passage of sperm, or prevent the sperm and egg from meeting. These methods include hormonal contraceptives, barrier methods like condoms and diaphragms, and intrauterine devices (IUDs).
Also Read:
- Phenotypic ratio for the offspring
- Genetic diversity types
- Barnacle example
- Heterotrophic bacteria examples
- Atp synthesis stages
- Do ribosomes make proteins
- Water miscible
- Do archaea have a cell wall
- Is mitochondrial dna inherited
- Do fungi have ribosomes

The TechieScience Core SME Team is a group of experienced subject matter experts from diverse scientific and technical fields including Physics, Chemistry, Technology,Electronics & Electrical Engineering, Automotive, Mechanical Engineering. Our team collaborates to create high-quality, well-researched articles on a wide range of science and technology topics for the TechieScience.com website.
All Our Senior SME are having more than 7 Years of experience in the respective fields . They are either Working Industry Professionals or assocaited With different Universities. Refer Our Authors Page to get to know About our Core SMEs.
